How to Boost Your Immune System to Fight Cancer
The human immune system helps to protect the body against illness and infection caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. This process is achieved by a collection of reactions and responses made by the body to damage these infected cells. It is also called immune responses.
This immune system is very crucial in cancer patients to help fight cancer. It identifies cancer as abnormal and destroys it, but this is not enough to rid the body of cancer altogether. In most cases, cancer will weaken this immune system because it spreads into the bone marrow that produces blood cells that fight against infections and cause the bone marrow to decrease its blood cell production.
When the immune system is unable to recognize these cells as abnormal, cellular growth will occur, causing uncontrolled growth and division of cells, leading to cancer.
The Importance of a Strong Immune System in Cancer
Cancer has been a serious and sensitive topic for both patients and doctors. Being diagnosed with cancer is frightening and tormenting, but due to the latest treatment methods, recovering from this disease is increasingly possible. Living with cancer often brings an initial psychological crisis, but surprisingly it affects not only you but also your family and others close to you.
Cancers, especially genetic cancer, can’t be prevented, so it is essential to be proactive about your health. If you’re diagnosed with cancer, some individual lifestyles will help improve your cancer care, which includes managing stress. Reducing your stress level can help you to maintain physical and mental health; you can use relaxation techniques such as meditation and yoga. Getting enough sleep is also crucial for patients living with cancer; this will help improve their health, mood, and coping ability. Also, it is best to limit exposure to toxins that can increase one’s risk of being exposed to other deadly diseases.
Healthy Feeding Habits
A healthy feeding habit is critically important and can help manage cancer side effects, improve health, and quick recovery. Some tips to help you develop a good and healthy diet include:
- Consuming assorted types of vegetables in all your meals. Vegetables are essential and should not just be a side dish but the centerpiece of your meal.
- Consuming foods rich in fiber like grains, beans, peas, nuts, and seeds.
- Consuming less red meat, like pork, lamb, goat, and bison.
- Including probiotic and prebiotic foods to support a healthy gut. Probiotic foods include yogurt or other fermented vegetables, and prebiotic foods include raw or cooked onions, dandelion greens, and legumes.
- Avoiding processed and canned foods.
- Avoiding foods high in calories and low in nutrients like fruit-flavored drinks, sodas, candies, and sweets.
- Cutting down on the excessive intake of alcohol.
Exercise and Cancer Care
Other routines that can help improve cancer care include regular exercise. Regular exercise helps to control fatigue, muscle tension, and anxiety in those with cancer, and it is essential, especially during and after cancer treatment, to keep fit and avoid gaining unnecessary weight.
Cancer Treatment Options
There are many cancer treatment options for different types of cancers. Cancer treatments depend on the type and how advanced it is. Some patients with cancer will only have one treatment option, while others will end up with a combination of more than one treatment technique depending on the type and stage of cancer.
Curing cancer is one of the significant challenges of the 21st century. However, few advances to tame the immune system are getting closer to a future where cancer can be a curable disease.
Advances in Immunotherapy
Although cancer treatment is dependent on the stage and type, we need a wide range of therapies that work on a cellular level, like NK cell and stem cell therapies, wide enough to cover the whole spectrum of cancer. Cancer therapies involving the immune system are believed to be a milestone for cancer treatment advances and the development of multiple immune cells as a therapeutic tool.
Our knowledge of cancer has dramatically improved in recent years. It seems increasingly evident that there has been a surge of new technologies, and these technologies could make a great impact on the way we treat cancer, taking us closer to finally curing this deadly disease.
NK Cells: A Promising Cancer Treatment
What Are NK Cells?
One of these promising cancer treatment advances is the natural killer (NK) cell-based immunotherapy. Natural killer cells have emerged as the newest promising therapeutic approach to cancer. Our understanding of the biological processes that take place in cancer is increasing rapidly, leading to this new type of targeted treatment and therapeutic approach. It is hard to overstate the possible importance of NK cells in the future of cancer.
How NK Cells Work
Modern research has shown that NK cells are a type of treatment that stimulates a person’s immune system to fight cancer, and this may give room for a greater number of chances to beat cancer for good. NK cells are also known for their ability to target cancer stem cells, making these cancer stem cells visible to the immune system.
NK cells were first identified in the 1970s as a unique lymphocyte subset that can recognize and kill abnormal cells without prior sensitization to specific tumor antigens, thus preventing the growth of many cancers. During the late 1980s, it was observed that NK cells could destroy a lymphoma cell line that had lost MHC class I surface molecules while the original MHC class I+ cells were resistant to lysis. This led to the formation of the “missing self-hypothesis,” which states that NK cells can sense the absence of “self” MHC class-I molecules on target cells. In recent years, the hypothesis was confirmed by the inhibitory and activating NK cell receptors.
Mechanisms of NK Cell Action
This discovery indicates that autologous cells are not killed by NK cells, thanks to an appropriate expression of all self-HLA alleles, preventing the killing of autologous cells. In contrast, a wide spectrum of cancer types can be killed due to the loss of HLA molecules and the expression/overexpression of ligands for NK cell activating receptors.
NK cells first recognize the tumor cells via stress or danger signals from their sensors. Then, the activated NK cells directly decimate the target tumor cells through at least four mechanisms: cytoplasmic granule release, death receptor-induced apoptosis, effector molecule production, or antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC).
Furthermore, NK cells act as regulatory cells when they reciprocally interact with dendritic cells (DCs) to improve their antigen uptake and presentation. This action helps in facilitating the generation of antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses that are vital in dictating foreign invasion and tumor cells.
By producing cytokines such as IFN-γ, activated NK cells induce CD8+ T cells to become CTLs. Activated NK cells can also help in the differentiation of CD4+ T cells toward a Th1 response and promote CTL differentiation. Cytokines produced by NK cells might even have the unique ability to regulate antitumor cells, making them more proactive.
Enhancing NK Cell Therapy
Accordingly, the cytokine gene transfer approach induces NK cell proliferation, increasing survival capacity, further enhancing their activation, and making them more potent in malignant cell multiplication dictation. NK cell scientists have assured that by using NK cell lines and modifying genes such as IL-2, IL-12, IL-15, and stem cell factor (SCF), they have demonstrated the ability of NK cells to restore their cytotoxic capacity as well as increase their proliferative rate, survival ability, and in vivo antitumor activity. However, the specificity of NK cells is still limited, and studies are still passing through phases. The approach focuses on retargeting NK cells to tumor cells by gene transfer of chimeric tumor-antigen specific receptors.
NK therapy is promising research; it raises the prospect of a “one-end-solution” to many different types of cancers across the globe. If the studies and experiments work out well, NK cells will be able to increase the activity of CD4+, CD19, and other important disease-fighting cells of the body.
The Future of NK Cell Therapy
There is no doubt that this is an unimaginable feat, both in advancing our basic knowledge about regenerative medicine and for the possibility of future cancer treatment advances.
- Published in Corporate News / Blog
Stem cell treatment could offer one-end-solution to Diabetes
Insulin-producing cells grown in the lab could provide a possible cure for the age-old disease, diabetes.
Understanding Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that destroys insulin-producing pancreatic beta cells, leading to dangerously high blood glucose levels. Patients often require insulin administration and other medications to manage blood sugar levels. For those who struggle with blood sugar control, beta-cell transplants are an option, but they require immunosuppressive drugs.
Breakthroughs in Stem Cell Research
A research group at Harvard University reported using insulin-producing cells derived from human embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and induced pluripotent stem cells to lower blood glucose levels in mice. Laboratories worldwide are making rapid progress in human stem cell technology to develop cells functionally equivalent to beta cells and other pancreatic cell types. Novel biomaterials are being developed to encapsulate these cells, protecting them from the immune system without the need for immunosuppressants.
Major Investments in Diabetes Treatment
Pharmaceutical companies and venture capital firms have invested over $100 million in leading biotechnology companies to bring stem cell treatments into clinical use. Prominent companies include:
- Semma Therapeutics
- Sigilon Therapeutics
- ViaCyte
Transforming Human Stem Cells into Insulin-Producing Cells
Researchers at UC San Francisco have successfully transformed human stem cells into mature insulin-producing cells, a significant breakthrough in developing a cure for Type 1 Diabetes (T1D). These cells mimic the function of pancreatic beta cells and offer hope for creating transplantable cells for patients with diabetes.
What is T1 Diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is characterized by the destruction of insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, typically starting in childhood. Without insulin, blood glucose levels can spike, causing severe organ damage and potentially leading to death. The condition can be managed with insulin shots, but serious health complications often persist, such as kidney failure, heart disease, and stroke.
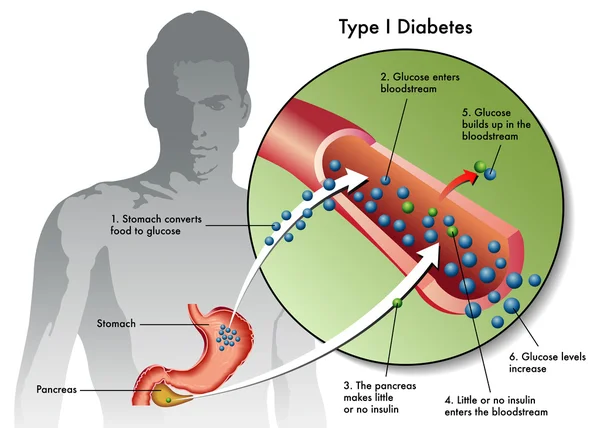
Making Insulin-Producing Cells from Stem Cells
Diabetes can be treated through a pancreas transplant or donor cell transplantation, but both methods rely on deceased donors. Scientists have struggled to produce mature beta cells responsive to blood glucose and capable of secreting insulin correctly. However, recent breakthroughs at UCSF have achieved this transformation in mice, marking a critical step toward human application.
Protecting Stem Cell Therapies from the Immune System
Delivering stem cell therapies requires protection from immune attacks while maintaining cell functionality. Companies are exploring two main strategies:
- Microencapsulation: Immobilizing cells individually or in small clusters within biocompatible gel blobs.
- Macroencapsulation: Placing larger numbers of cells into a larger, implantable device.
Companies Leading the Way
- ViaCyte: Partnered with Johnson & Johnson, using microencapsulation in clinical trials.
- Semma: Developing both macro- and microencapsulation methods, readying for clinical trials.
- Sigilon: Utilizing gel-based spheres for encapsulation, in collaboration with Eli Lilly.
Conclusion
Stem cell treatment holds the potential to revolutionize diabetes care, offering a one-end solution to managing and potentially curing the disease. With significant investments and ongoing research, the future of diabetes treatment looks promising. Researchers and companies are making strides in developing effective and safe stem cell therapies, bringing hope to millions worldwide.
- Published in Corporate News / Blog

![Secondary-Diabetes[1]](https://www.stemcellsgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/Secondary-Diabetes1-460x260_c.png)
