The History of Research on Adult Stem Cells: We’ve Come a Long Way
Introduction to Adult Stem Cells
Adult stem cells, also known as somatic stem cells, are undifferentiated cells found among differentiated cells in tissues or organs. They play a crucial role in tissue maintenance and repair.
Types and Functions of Adult Stem Cells
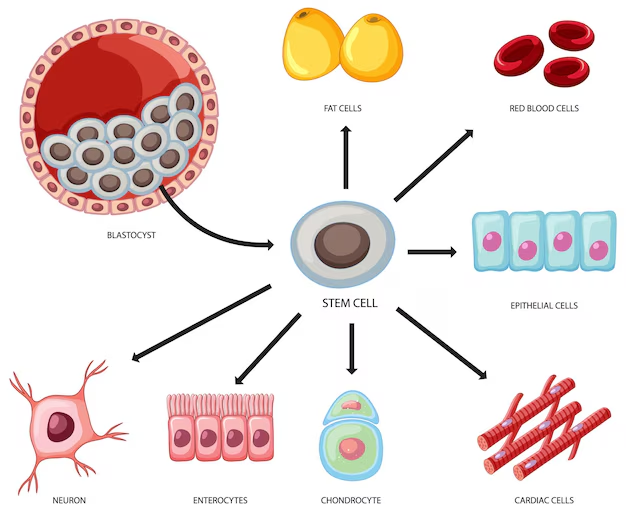
Bone Marrow Stem Cells
- Hematopoietic Stem Cells: Responsible for forming all blood cell types.
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Can differentiate into bone, cartilage, fat cells, and support blood formation.
Brain and Heart Stem Cells
Recent discoveries have identified stem cells in unexpected locations like the brain and heart, challenging previous beliefs and expanding potential applications in transplantation therapies.
Historical Development of Adult Stem Cell Research
Early Discoveries
In the 1950s, researchers identified hematopoietic stem cells in bone marrow, marking the beginning of significant research into adult stem cells.
Advances Over Decades
- 1960s: Discovery of neural stem cells in the brain.
- 1990s: Confirmation of adult brain’s capability to generate neurons and other cell types.
Distribution of Adult Stem Cells in the Body

Adult stem cells are found in various organs and tissues, residing in specific niches critical for their function and activation in response to tissue repair needs or disease.
Methods to Identify Adult Stem Cells
Scientists employ several techniques:
- Labeling and Differentiation: Using molecular markers to track specialized cell types generated.
- Transplantation Studies: Removing and labeling cells, then transplanting them to observe tissue repopulation.
Future Directions in Adult Stem Cell Research
Ongoing research aims to:
- Further characterize and manipulate adult stem cells for therapeutic purposes.
- Explore personalized medicine applications using stem cell technologies.
Conclusion
The study of adult stem cells has evolved significantly, offering promising avenues for understanding and treating various diseases. Continued research holds potential for transformative advancements in regenerative medicine.
- Published in Corporate News / Blog
Stem Cell Research and Stem Cell Therapy: When can stem cells be used to treat patients?
Understanding Stem Cell Research
Stem cells possess the unique ability to differentiate into various specialized cell types in the body, making them invaluable for regenerative medicine. They play a crucial role in replenishing damaged tissues throughout an individual’s life.
Types of Stem Cells in Research
- Embryonic Stem Cells: Derived from the inner cells of a blastocyst, these cells have the potential to form any type of cell in the body.
- Adult Stem Cells: Found in various tissues, these cells contribute to tissue repair and maintenance.
- Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs): Reprogrammed from adult cells to exhibit embryonic-like properties, offering new avenues for research and therapy.
Applications of Stem Cells in Disease Treatment
Stem cell research holds promise for treating a wide array of diseases, including diabetes and heart disease, by harnessing their regenerative capabilities.
Challenges and Research Advances
- Laboratory Studies: Used to understand fundamental properties and differentiation mechanisms of stem cells.
- Drug Screening: Stem cells serve as models to test new drugs and study normal growth processes and disease mechanisms.
Ethical Considerations and Guidelines
The Declaration of Helsinki guides ethical practices in stem cell research involving human subjects, emphasizing informed consent and the need for ongoing evaluation of experimental interventions.
Clinical Translation of Stem Cell Therapies
- Regulatory Framework: Clinical trials are essential to evaluate the safety and efficacy of stem cell-based treatments.
- Phases of Clinical Trials: From initial safety assessments (Phase 0) to post-marketing studies (Phase IV), each phase plays a crucial role in determining treatment viability.
Future Directions in Stem Cell Research
Continued advancements in stem cell research are expected to expand our understanding of cellular regeneration and pave the way for innovative therapies.
- Published in Corporate News / Blog