Introduction
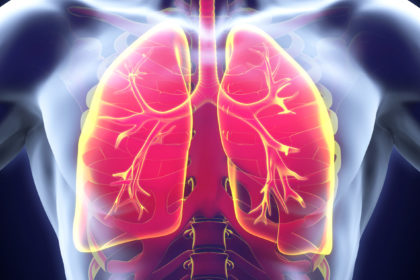
Chronic lung diseases, including COPD, bronchitis, emphysema, and asthma, are significant causes of mortality in the U.S., highlighting the urgent need for advanced treatments.
Stem Cells in the Lung
Types and Functions of Lung Stem Cells
Human lungs are complex organs comprising:
- Conducting Airway Tubes: Includes trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles.
- Gas Exchange Regions: Alveolar spaces crucial for oxygen exchange.
Role of Progenitor Cells
Progenitor cells like tracheal basal cells and alveolar type 2 cells play a vital role in maintaining lung health by replacing old or damaged cells.
Diversity of Lung Stem Cells
Embryonic and adult lung stem cells contribute differently:
- Research indicates their role in lung development and regeneration, with potential implications for disease treatment.
Current Research on Lung Stem Cell Therapies
Adult Mesenchymal Stem Cells (hMSCs)
hMSCs are pivotal in:
- Immunomodulation: Regulating immune functions and secreting bioactive molecules for anti-inflammatory and regenerative effects.
- Versatility: Capable of generating various cell types, potentially aiding in lung tissue repair.
Insights into Lung Disease Causes
Understanding lung stem cell biology enhances knowledge of disease mechanisms like COPD, paving the way for innovative treatments.

Future Prospects of Lung Stem Cell Therapies
Translational Research and Clinical Applications
Ongoing studies aim to:
- Identify and characterize lung stem cells in humans, advancing potential clinical applications.
- Explore personalized medicine approaches using lung stem cells for targeted therapies.
Conclusion
Progress in lung stem cell research holds promise for developing effective therapies to combat chronic lung diseases, offering hope for improved patient outcomes and quality of life.