How Clinical Trials on Stem Cell Therapies Work, and Where to Find Them
Introduction to Stem Cell Clinical Trials
Stem cell clinical trials play a crucial role in evaluating the safety and efficacy of new treatments. Accessing information about these trials is facilitated through dedicated registries like ClinicalTrials.gov and the WHO International Clinical Trial Registry Platform.
Key Resources for Stem Cell Clinical Trials
ClinicalTrials.gov
- Purpose and History: Established under the FDA Modernization Act to provide comprehensive information on clinical studies.
- Accessibility: Offers updated information directly from study sponsors or principal investigators.
WHO International Clinical Trial Registry Platform
- Supplementary Information: Provides additional details complementing ClinicalTrials.gov, enhancing accessibility and usability for researchers and participants.
Geographic Distribution and Focus Areas of Stem Cell Trials
- Location Trends: Predominantly conducted in the U.S. followed by Europe, as evidenced by data from ClinicalTrials.gov.
Phases of Clinical Trials
Global Distribution
Overview of Trial Phases
- Phase 0 to Phase IV: Sequential stages from initial safety assessments to post-marketing studies, each serving distinct purposes in drug development and evaluation.
Types of Stem Cell Clinical Trials

Interventional Studies
- Purpose: Volunteers are assigned interventions to evaluate biomedical or health outcomes based on specific protocols.
- Inclusion of Observational Studies: Descriptions of observational studies and expanded access programs for investigational drugs are also included.
Funding Sources for Stem Cell Trials
Analysis of Funding
- Primary Funders: Includes the National Institutes of Health (NIH), other federal agencies, industry partners, and diverse entities such as universities and community-based organizations.
- Impact of Funding: Highlights the diversity of financial support influencing stem cell research outcomes and accessibility.
Conclusion
Understanding the structure and resources of stem cell clinical trials is crucial for both researchers and participants seeking innovative treatments. Access to comprehensive trial information supports informed decision-making and advances in medical research.
- Published in Corporate News / Blog
Stem Cell Research and Stem Cell Therapy: When can stem cells be used to treat patients?
Understanding Stem Cell Research
Stem cells possess the unique ability to differentiate into various specialized cell types in the body, making them invaluable for regenerative medicine. They play a crucial role in replenishing damaged tissues throughout an individual’s life.
Types of Stem Cells in Research
- Embryonic Stem Cells: Derived from the inner cells of a blastocyst, these cells have the potential to form any type of cell in the body.
- Adult Stem Cells: Found in various tissues, these cells contribute to tissue repair and maintenance.
- Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs): Reprogrammed from adult cells to exhibit embryonic-like properties, offering new avenues for research and therapy.
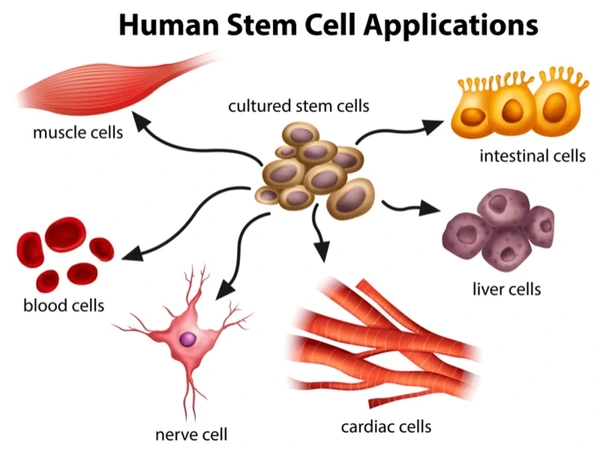
Applications of Stem Cells in Disease Treatment
Stem cell research holds promise for treating a wide array of diseases, including diabetes and heart disease, by harnessing their regenerative capabilities.
Challenges and Research Advances
- Laboratory Studies: Used to understand fundamental properties and differentiation mechanisms of stem cells.
- Drug Screening: Stem cells serve as models to test new drugs and study normal growth processes and disease mechanisms.
Ethical Considerations and Guidelines
The Declaration of Helsinki guides ethical practices in stem cell research involving human subjects, emphasizing informed consent and the need for ongoing evaluation of experimental interventions.
Clinical Translation of Stem Cell Therapies
- Regulatory Framework: Clinical trials are essential to evaluate the safety and efficacy of stem cell-based treatments.
- Phases of Clinical Trials: From initial safety assessments (Phase 0) to post-marketing studies (Phase IV), each phase plays a crucial role in determining treatment viability.
Future Directions in Stem Cell Research
Continued advancements in stem cell research are expected to expand our understanding of cellular regeneration and pave the way for innovative therapies.
- Published in Corporate News / Blog
Gordie Howe’s Stem Cells Treatments Support a Growing Appeal for These Therapies Among Athletes and Baby Boomers
The Story of Gordie Howe’s Stem Cell Treatment
In October 2014, Gordie Howe, the legendary hockey player, faced a life-threatening stroke that left him severely debilitated. Despite medical efforts, including an experimental stem cell treatment in Mexico, his condition continued to deteriorate. However, after receiving neural and mesenchymal stem cells, Howe showed remarkable signs of improvement, including regaining mobility and cognitive function.
The Impact of Stem Cell Therapy on Gordie Howe’s Recovery
- Experimental Treatment: Howe’s treatment involved injecting neural and mesenchymal stem cells into his spinal canal, aiming for brain repair and anti-inflammatory benefits.
- Recovery Milestones: Within hours of the procedure, Howe exhibited unexpected improvements, such as walking unaided for the first time since his stroke.
Stem Cell Therapy: Appeal Among Athletes and Baby Boomers
Athletes’ Interest in Stem Cell Therapy
Athletes, prone to injuries and degenerative conditions, increasingly turn to stem cell therapy for its potential regenerative properties. Icons like Bart Starr and John Brodie have also pursued such treatments.
Growing Popularity Among Baby Boomers
The aging population, particularly baby boomers, seeks stem cell therapies to address age-related ailments such as joint degeneration and chronic conditions.
Controversies and Regulatory Challenges

Despite its appeal, stem cell therapy faces scrutiny due to regulatory issues and varying international standards. The FDA is developing guidelines to regulate these treatments, distinguishing between approved clinical trials and unauthorized clinics.
Regulatory Landscape and FDA Guidelines
- Current FDA Oversight: Most stem cell therapies require FDA approval, with exceptions for minimally manipulated cells.
- Unauthorized Clinics: Concerns persist over unauthorized stem cell clinics operating outside regulatory frameworks.
Future Directions and Considerations
As research and public interest in stem cell therapy continue to grow, ongoing debates over efficacy, safety, and regulatory oversight shape its future in medical practice.
- Published in Corporate News / Blog
Stem Cell Researchers Discover Stem Cells That Might Repair Skull, Face Bones
Breakthrough in Stem Cell Research for Bone Repair
Scientists have made significant progress in using stem cells to potentially replace damaged skull and facial bones, crucial for patients recovering from head trauma or undergoing reconstructive surgery after cancer treatments.
Discovery of Skull and Facial Bone Repair Capabilities
Researchers at the University of Rochester Medical Center, led by Takamitsu Maruyama, have identified and isolated stem cells with the ability to regenerate these specific bones in mice. This breakthrough offers hope for treating conditions like craniosynostosis, a congenital skull deformity that impacts brain development.

Insights from Bone Formation and Regeneration Studies
The study focused on the role of the Axin2 gene in bone formation, crucial for understanding how these stem cells contribute to bone repair. The research also explored mutations linked to craniosynostosis in mice, revealing distinct populations of stem cells unique to skull bones.
Potential Applications in Bone Disease Detection
Beyond repair, identifying these specialized stem cells could aid in diagnosing bone diseases associated with stem cell abnormalities, offering new insights for medical professionals.
Publication and Impact
Published in Nature Communications on February 1, this research marks a significant advancement in bone regeneration therapies, paving the way for future clinical applications and further studies in human subjects.
- Published in Corporate News / Blog
German Stem Cell Scientists Develop 3-D “Mini-retinas” –New Hope for Restoring Sight in Patients with Retinal Degeneration Caused by Diabetes and Inherited Disorders.
Breakthrough in Retinal Regeneration Using 3D Organoids
Protocol for 3D Mini-retinas

German researchers have achieved a significant breakthrough in stem cell technology focused on restoring sight through the development of 3D retina organoids. Published in Stem Cell Reports in March, this study leverages the self-organizing properties of stem cells to create complex, multi-cellular tissue structures.
The innovative protocol involves dividing organoids grown from stem cells into three half-moon shaped pieces during early eye development. This technique facilitates the growth of fully functional retinal cells within each segment, including cone photoreceptors crucial for high acuity and color vision. These advancements are particularly promising for patients suffering from retinal degenerative disorders caused by diabetes and inherited conditions.
Advantages of 3D Retinal Organoids
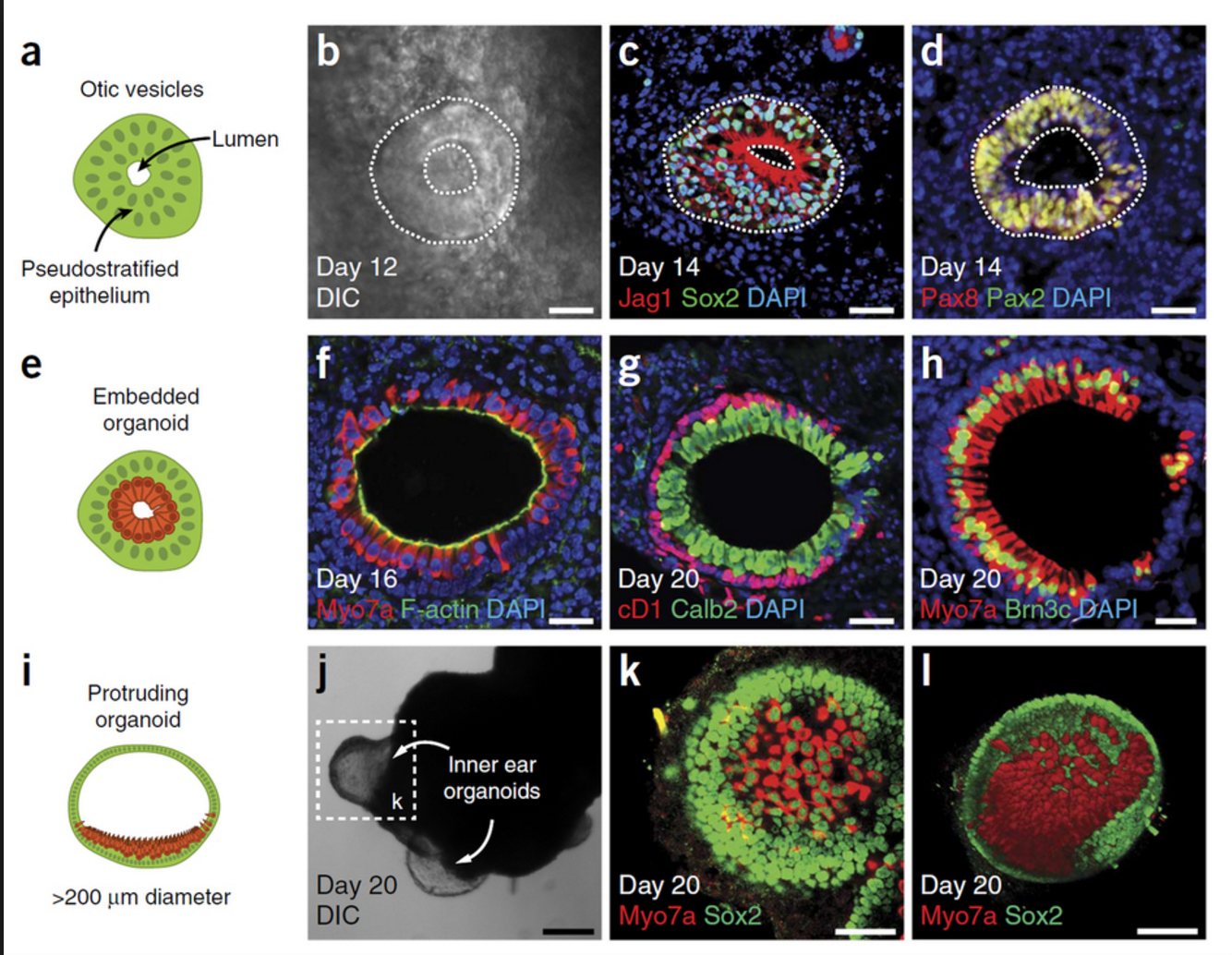
The development process not only enhances the production yield of retinal organoids by up to four times compared to previous methods but also allows for the formation of more realistic tissue structures resembling natural retinal tissue during development.
Applications in Retinal Disease Research
According to senior author Mike Karl from the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE) and the Center for Regenerative Therapies (CRTD) at Technische Universität Dresden, the versatility of 3D mini-retinas extends beyond replication of retinal tissue. It offers diverse opportunities for studying retinal diseases and potential therapeutic interventions.
Future Directions in Organoid Research
Karl’s team aims to enhance the complexity of mini-retinas by incorporating blood vessels and studying the regeneration capabilities and neural cell functions specific to the human retina. This approach not only furthers understanding of retinal diseases but also holds promise for developing personalized treatments.
Insights and Comparative Studies
Comparative studies between human pluripotent stem cell-derived retina organoids and in vivo mouse retina underscore the potential of this novel organoid protocol to model retinal diseases effectively.
- Published in Corporate News / Blog
Stem Cell Treatments Normally Used for Cancer Patients are Helping Multiple Sclerosis Patients
Overview of Stem Cell Transplant for MS Patients
Recent reports from the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) highlight the transformative effects of stem cell transplant treatments originally used for cancer patients on individuals suffering from Multiple Sclerosis (MS) in the UK. According to a January 18, 2016 report, this innovative approach has shown promising results in restoring mobility and reversing disability in MS patients.
Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT)
The treatment, known as autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), involves the infusion of the patient’s own stem cells harvested from bone marrow. This procedure aims to rebuild the immune system, potentially resetting it to a state before it caused MS-related damage.
Testimonials and Clinical Results
Professors Basil Sharrack and John Snowden from Sheffield’s Royal Hallamshire Hospital emphasize the profound impact of HSCT on MS patients. Patients like Steven Storey, who experienced significant disability progression prior to treatment, have reported remarkable improvements in mobility and quality of life post-transplant.
Steven Storey’s Journey
Steven Storey, diagnosed with MS in 2013, transitioned from being an athlete to wheelchair-bound within a year. Following HSCT, he regained movement in his toes within days and achieved unaided standing after four months. While still using a wheelchair, Storey’s progress is described as astounding, allowing him to swim, cycle, and aspire to walk again.
The MIST International Clinical Trial
The Royal Hallamshire Hospital, alongside institutions in the US, Sweden, and Brazil, participates in the MIST trial. This international study evaluates the long-term benefits of HSCT on patients with relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS), aiming to establish its efficacy as a standard treatment option.
Future Prospects and Research
Prof Richard Burt of Northwestern University leads the MIST trial, pioneering HSCT for MS treatment since 1995. Despite challenges from the pharmaceutical and academic sectors, early studies have shown promising neurological disability reductions, with ongoing research poised to validate these findings further.
Conclusion and Outlook
As ongoing research continues to validate the potential of HSCT in treating MS, stakeholders like Emma Gray, M.D., head of clinical trials at the UK’s MS Society, emphasize its life-changing impacts highlighted by real patient experiences. The outcomes from the MIST trial, expected in 2018, could potentially integrate HSCT into the standard healthcare protocols for MS patients in the UK.
- Published in Corporate News / Blog
Our Friend MSCs (Mesenchymal Stem Cells)—Bringing New Life to Old Bones
Understanding MSCs and Their Role in Osteoporosis Treatment
Researchers from the University of Toronto and The Ottawa Hospital have explored the potential of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in treating osteoporosis. MSCs are versatile stromal cells capable of differentiating into bone cells (osteoblasts), cartilage cells (chondrocytes), muscle cells (myocytes), and fat cells (adipocytes).
Research Insights: MSCs Reverse Osteoporosis in Mice
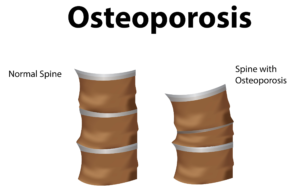
In a groundbreaking study published in Stem Cells Translational Medicine, researchers injected healthy MSCs into mice with osteoporosis. Over six months—a significant period in a mouse’s lifespan—the damaged, brittle bones of the mice were replaced with healthy bone tissue. This restoration underscores the regenerative potential of MSCs in treating bone disorders.
Clinical Applications and Future Directions
This discovery raises hopes for new osteoporosis treatments in humans. Early trials involving elderly patients in the US have shown promising results, with ongoing studies assessing improvements in bone health through biological markers in blood samples.
The Global Impact of Osteoporosis
Globally, over 200 million people suffer from postmenopausal or age-related osteoporosis, leading to approximately 8.9 million bone fractures annually. Current treatments, like Teriparatide, offer temporary relief, highlighting the urgent need for more effective, long-term solutions.
Key Researchers and Publications
Dr. William Stanford, senior scientist at The Ottawa Hospital Research Institute and professor at the University of Ottawa, led the study linking MSC defects to age-related osteoporosis in mice. Co-author Dr. John E. Davies, professor at the University of Toronto, contributed to the study’s publication in Stem Cells Translational Medicine on March 17, 2016.
- Published in Corporate News / Blog
Stem cells and Platelet Rich Plasma Therapies Look Promising for Treating a Variety of sports-related injuries
Advancements in Stem Cell Therapies for Sports Injuries
Stem cell therapies have garnered significant attention among researchers aiming to leverage these cells’ regenerative properties for treating sports injuries. Stem cells, naturally occurring in the body, facilitate inflammation modification and promote healing of damaged tissues.
Mayo Clinic’s Approach with PRP for Injured Athletes
Researchers at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, are pioneering treatments that combine stem cells with platelet-rich plasma (PRP). PRP, derived from the patient’s own blood, concentrates platelets to stimulate healing and reduce inflammation at the injury site. This personalized approach tailors PRP preparations to meet individual patient needs.
Utilizing Bone Marrow Stem Cells for Enhanced Healing
Mayo Clinic researchers harvest stem cells from the patient’s bone marrow, which contains potent therapeutic cells. After concentration to eliminate unwanted components, these stem cells are reintroduced into the injured area. This method harnesses stem cells’ ability to regenerate tissues, thereby accelerating the healing process for sports injuries.
Innovations by Joseph Purita, M.D., in Orthopedic Stem Cell Therapies
Joseph Purita, M.D., an esteemed osteopathic surgeon associated with Global Stem Cells, has pioneered the use of stem cells and PRP to treat professional athletes. His groundbreaking treatments have spotlighted orthopedic stem cell therapies globally, emphasizing their efficacy in sports injury rehabilitation.
Stem Cell Treatments Targeting Muscle Repair
Muscle injuries, prevalent in sports, often involve damage to myoblasts—embryonic cells responsible for muscle fiber repair. Researchers are exploring how stem cells, particularly mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), can enhance muscle tissue regeneration. MSCs, isolated from various patient tissues including fat, produce proteins that promote healing and tissue-specific stem cell activation.
Future Directions in Sports Injury Therapies
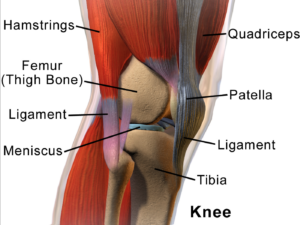
Ongoing research aims to optimize stem cell and PRP therapies for broader applications in sports medicine. Discoveries such as enhancing muscle tissue repair through rejuvenating older satellite cells highlight potential future treatments.
- Published in Corporate News / Blog
Stem Cells are Gaining Momentum Among Smart Investors
The Rise of Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine Investments
Stem cell and regenerative medicine companies are capturing the attention of serious investors who are closely monitoring advancements in biotechnology and the rapid integration of these technologies into clinical settings worldwide.
Demand for Stem Cell Therapies and Medical Tourism Trends
Healthcare consumers increasingly seek alternatives to invasive and costly conventional treatments offered by Western medicine and pharmaceuticals. Stem cell therapies have met this demand, prompting patients from the US and Europe to seek treatments abroad due to regulatory constraints at home. This has fueled the growth of medical tourism and direct marketing of regenerative medicine therapies.
Global Expansion and Investment in Regenerative Medicine
Stem cell companies are expanding globally, driven by escalating patient demand and a surge in positive clinical trials and media coverage. Despite regulatory challenges, these companies are reshaping modern medicine, attracting capital from investors who foresee the transformative potential of stem cell research and therapies.
Strategic Investments and Market Growth
Investment in gene therapies, genetically modified cell therapies, and regenerative medicine has seen exponential growth, with substantial contributions from venture capital, public equity markets, and partnerships with pharmaceutical and biotechnology giants. This influx of capital underscores the expanding maturity and potential of these technologies in healthcare.
Future Outlook and Milestones in Regenerative Therapies
The forecast for regenerative medicine includes significant upcoming milestones in clinical data, FDA approvals, and biologics licensing applications (BLAs). Investors are recognizing the pivotal role of cell therapies in revolutionizing healthcare, akin to the impact of groundbreaking scientists in previous medical eras.
Conclusion
Investors are poised to support the future leaders in regenerative medicine, paralleling the rise of tech giants like Apple and Microsoft in their early stages. The value of cellular therapies extends beyond patient outcomes to potential cost savings and transformative shifts in healthcare delivery.
- Published in Corporate News / Blog
Demand for Physicians Who Provide Stem Cell Therapies is Growing
The Shift Towards Stem Cell Therapies
There is a rising global movement among patients with degenerative diseases and orthopedic conditions seeking alternatives to conventional treatments through stem cell therapies. Frustrated by invasive surgeries, destructive procedures, and pharmaceutical side effects, more patients are turning to the promising field of regenerative medicine.
Global Stem Cells Group’s Leadership in Stem Cell Treatments
Global Stem Cells Group (GSCG) leads in stem cell research, training, and patient services worldwide. Despite regulatory challenges, GSCG provides stem cell treatments internationally, addressing the increasing demand for innovative medical solutions.
Focus on COPD Treatment with Stem Cells

GSCG’s research includes pioneering stem cell treatments for COPD, a chronic respiratory disease affecting millions globally. Studies using adipose-derived stem cells have shown promising results in improving patients’ quality of life and respiratory functions.
Innovative Approaches to Congestive Heart Failure
In treating congestive heart failure, GSCG employs adipose-derived stem cells to enhance blood flow and rejuvenate damaged heart tissue. Initial results indicate significant improvements in exercise capacity and overall cardiac function post-treatment.
Advancements in Critical Limb Ischemia
GSCG’s groundbreaking trial for critical limb ischemia, targeting diabetic patients with non-healing wounds, demonstrated a remarkable 75% success rate in preventing amputations. Stem cell therapies promote angiogenesis and tissue regeneration, offering hope for severe vascular conditions.
Case Study: Healing Non-Healing Wounds
A compelling case at the Regenerative Medicine Institute highlighted successful treatment of a non-healing leg ulcer with adipose stem cells, avoiding amputation and restoring normal blood flow—a testament to the potential of stem cell therapies in complex medical cases.
The Role of Physicians in Regenerative Medicine
Physicians equipped with stem cell certification can significantly impact patient outcomes and practice revenue. Regenerative medicine is reshaping healthcare delivery by offering natural, minimally invasive treatments with fewer side effects than traditional pharmaceuticals.
- Published in Corporate News / Blog