In the realm of regenerative medicine, exosomes derived from umbilical cord stem cells are gaining significant attention. These nano-sized vesicles play a crucial role in cell-to-cell communication and have shown immense therapeutic potential. This article delves into the origins, functions, and promising applications of umbilical cord stem cell-derived exosomes.
What Are Exosomes?
Exosomes are small extracellular vesicles, typically 30-150 nm in diameter, secreted by various cell types. They are involved in intercellular communication, transferring proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids between cells. Exosomes are known to influence numerous physiological processes, including immune responses, inflammation, and tissue repair.
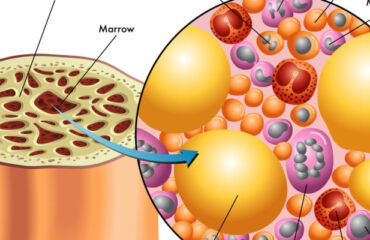
Umbilical Cord Stem Cells: A Rich Source
Umbilical cord stem cells, particularly mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), are a rich source of exosomes. These stem cells are easily accessible, and have a high proliferative capacity. The exosomes derived from umbilical cord MSCs are packed with bioactive molecules that exhibit potent regenerative properties.
Mechanism of Action
Exosomes exert their therapeutic effects through several mechanisms:
- Cellular Communication: Exosomes facilitate communication between cells by transferring bioactive molecules, which can modulate the behavior of recipient cells.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: They help reduce inflammation by modulating the immune response.
- Tissue Repair and Regeneration: Exosomes promote tissue repair by enhancing cell proliferation, migration, and differentiation.
Therapeutic Applications
1. Wound Healing
Exosomes from umbilical cord stem cells have shown to accelerate wound healing by promoting angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels), collagen synthesis, and reducing scar formation.
2. Cardiovascular Diseases
Studies have demonstrated that exosomes can improve cardiac function following myocardial infarction by enhancing cardiac cell survival, reducing fibrosis, and promoting angiogenesis.
3. Neurological Disorders
Exosomes have the potential to treat neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s by delivering neuroprotective agents, reducing neuroinflammation, and promoting neuronal survival.
4. Liver Diseases
Exosome therapy is emerging as a promising treatment for liver diseases. They can help in the regeneration of liver tissue, reduce fibrosis, and improve overall liver function.
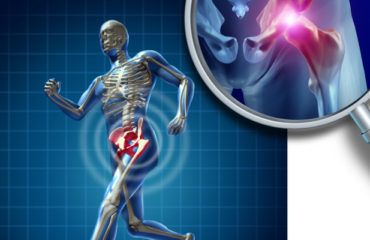
5. Orthopedic Applications
In orthopedic medicine, exosomes can aid in the healing of bone fractures, cartilage damage, and osteoarthritis by promoting the differentiation of stem cells into bone and cartilage cells.
6. Aesthetic Uses
Exosomes derived from umbilical cord stem cells are making waves in the field of aesthetics for their skin rejuvenation capabilities. They can:
- Promote Collagen Production: Leading to firmer, more youthful-looking skin.
- Enhance Skin Elasticity: Improving skin texture and reducing fine lines and wrinkles.
- Accelerate Skin Repair: Aiding in the healing of acne scars and other skin blemishes.
- Reduce Inflammation: Helping to calm irritated skin and reduce redness.
Clinical Trials and Research
Numerous clinical trials are underway to evaluate the safety and efficacy of exosome-based therapies. These studies are exploring a wide range of applications, from treating chronic wounds to regenerative treatments for heart disease and aesthetic improvements.
Future Perspectives
The field of exosome research is rapidly evolving. Advances in isolation techniques, molecular profiling, and delivery systems are expected to enhance the therapeutic potential of exosomes. Personalized medicine, where exosomes are tailored to the needs of individual patients, is a promising future direction.
Challenges and Considerations
While the potential of exosome therapy is immense, several challenges need to be addressed:
- Standardization: Developing standardized protocols for exosome isolation, characterization, and storage.
- Safety: Ensuring the safety and minimizing the risk of adverse effects.
- Scalability: Producing exosomes on a large scale for clinical use.
Conclusion
Exosomes derived from umbilical cord stem cells hold immense promise in regenerative medicine, aesthetic treatments, and disease management. Their ability to modulate cellular communication and promote tissue repair makes them a powerful tool for various therapeutic applications. As research progresses, the translation of exosome therapy from bench to bedside is becoming increasingly feasible, heralding a new era in medical treatment.