Autoimmune disorders are conditions where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells, causing damage to tissues and organs. With over 80 known types, including diabetes type 1, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, celiac disease, and multiple sclerosis, these disorders affect millions worldwide.
Understanding Autoimmune Disorders
The exact causes of autoimmune disorders remain unclear, though triggers like viruses, bacteria, or certain medications may disrupt immune function, leading the body to attack its own tissues. Common targets include red blood cells, skin, connective tissues, blood vessels, and various glands.
Current Treatments and Limitations
Standard treatments for autoimmune disorders primarily involve immune-suppressing medications, which offer temporary relief but do not provide a cure. Researchers are therefore exploring alternative approaches, such as stem cell therapy, to address these conditions effectively.
The Use of Stem Cells in Autoimmune Disorders
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) in Immunomodulation
Research indicates that mesenchymal stem cells, derived from sources like bone marrow, exert immunological functions that help maintain immune balance. Studies, including one published in Arthritis Research and Therapy, highlight MSCs’ ability to regulate immune responses and potentially prevent tissue destruction [1].
Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs) for Severe Autoimmune Diseases
Studies, such as those conducted at Harvard Medical School, explore the use of hematopoietic stem cells in treating severe autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis. Transplantation of HSCs following immunosuppressive therapies has shown promise in achieving disease remission [2].
Neural Stem Cells (NSCs) in Multiple Sclerosis
In multiple sclerosis research, neural stem cells derived from the central nervous system demonstrate neuroprotective and immunomodulatory effects. Studies suggest these cells could potentially repair damaged nerve tissues and improve symptoms in MS patients [3].
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Research on rheumatoid arthritis indicates that mesenchymal cells derived from sources like the placenta possess immunosuppressive properties. Studies, such as those investigating human amnion mesenchymal cells, show promise in alleviating arthritis symptoms and reducing disease severity [4].
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite promising results, challenges remain in optimizing stem cell therapies for autoimmune disorders. Researchers must establish precise protocols and address issues like immune rejection and treatment efficacy in larger clinical settings.


Thank you Sir
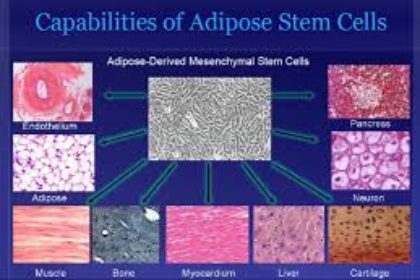
[…] studies are documenting the regenerative effects of fat grafting in areas no one suspected, such as autoimmune diseases and degenerative joint disease. Unlike bone marrow tissue, adipose tissue is easy to extract, it’s abundant, and it’s effective […]
[…] studies are documenting the regenerative effects of fat grafting in areas no one suspected, such as autoimmune diseases and degenerative joint disease. Unlike bone marrow tissue, adipose tissue is easy to extract, it’s abundant, and it’s effective […]