Introduction to Skin Stem Cell Research
Stem cell research has uncovered numerous groundbreaking discoveries over the years, many of which remain relatively unknown. This article highlights one such discovery related to skin stem cells and their critical role in regeneration and maintenance.
Discovery of Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b Proteins
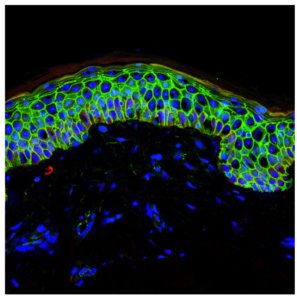
In a significant 2008 study published in “Cell Stem Cell,” researchers from the Catalan Institution for Research and Advanced Studies (CREA) identified two proteins—Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b—that play a crucial role in maintaining skin stem cells. Led by Salvador Aznar Benitah at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona), the study revealed that these proteins are essential for the activation and preservation of skin stem cells.
Function of Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b in Skin Stem Cells

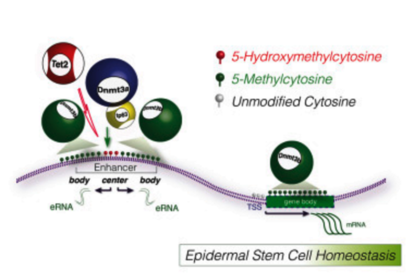
According to Benitah, head of the Stem Cells and Cancer lab at IRB Barcelona, without Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b, skin stem cells fail to activate and eventually diminish within the tissue. The proteins operate primarily on gene enhancers and super-enhancers, facilitating the expression of approximately 1,000 genes critical for the self-renewal of skin stem cells.
Genomic Insights and Mechanisms
Lorenzo Rinaldi, a researcher involved in the study, utilized advanced sequencing techniques to map the genomic distribution of Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b. This revealed their unexpected role in enhancing gene expression through DNA methylation, contrary to their previously known function in gene repression.
Link to Cancer Research
The study also highlighted implications for cancer research, noting that Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b are altered in various types of tumors, including leukemia, lung cancer, and colon cancer. The proteins’ role in DNA methylation and gene regulation suggests potential contributions to tumor development, warranting further investigation in cancer cell models.
Funding and Support
Funded by the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness and supported by several foundations and councils, including The European Council for Research (ERC) and the Fundació Marató de TV3, Benitah’s research underscores the importance of public and private partnerships in advancing stem cell and cancer research.
Conclusion
This study represents a significant advancement in understanding the molecular mechanisms governing skin stem cell maintenance and its implications for both regenerative medicine and cancer biology. Continued research into Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b promises to unveil new therapeutic strategies and insights into cellular regeneration and disease progression.